A Deep Dive into Multi-Level Marketing Dynamics


Intro
Multi-level marketing (MLM) often stirs up a whirlwind of emotions—some see it as a legitimate business model, while others cast it as a predatory scheme. But what exactly lies behind this polarizing investment strategy? In this exploration, we aim to dissect the complex layers of MLM, shedding light on the underlying structure, the psychological tricks at play, and the regulations that govern this realm. One of the biggest conundrums in the MLM world is understanding the distinction between a genuine opportunity and a potential scam; the stakes can be high, and the differences are often subtle.
Investors contemplating joining an MLM venture frequently find themselves ensnared in a web of exaggerated promises and complex hierarchies. In a landscape where everyone is vying for the limelight, making informed decisions becomes crucial. Understanding the lingo—what terms like "downline," "upline," and "commission structure" really mean—can make all the difference in discerning what’s real from what’s just smoke and mirrors. Furthermore, as technology continues to evolve, so too does the framework of MLM, raising compelling questions about ethics and integrity in a landscape that seems to be ever-changing.
With this in mind, let’s dive into the specifics of the investment aspect to set a solid foundation for our further discussions.
Defining Multi-Level Marketing
Defining multi-level marketing (MLM) is crucial in grasping what makes this business model both appealing and controversial. The very essence of MLM revolves around its structure and the methods through which it operates. By unpacking the components of MLM, investors can identify opportunities but also discern potential pitfalls that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Understanding MLM is about more than just knowing how it works; it invites a deeper reflection on the motivations behind such a system and the broader implications for potential participants. As the landscape of investment strategies continues to evolve, MLM has carved out a distinct niche that warrants a closer look.
What is Multi-Level Marketing?
Multi-Level Marketing, often referred to as network marketing, is a sales strategy where individuals earn income through their sales of products, as well as by recruiting others into the business. When these recruits make sales, the original distributor receives a commission. This creates a tiered structure, with income potential growing exponentially based on the network’s breadth.
To illustrate, imagine a pyramid with an individual at the top. As they recruit others, each new recruit also has the ability to add their own recruits, thus forming additional layers below. This layered approach not only incentivizes direct sales but also promotes the recruitment of new members, creating a rich metaphorical garden of income opportunities that can flourish, or wither, under various circumstances.
How Differs from Traditional Sales
Traditional sales models typically revolve around a straightforward exchange between a seller and a buyer. In these systems, the seller profits solely from their own sales efforts. MLM, however, operates on a different wavelength. It acts almost like a hybrid between direct sales and franchising.
This model introduces two primary elements that differ from traditional sales:
- Recruitment Focus: The emphasis is not only on direct product sales but also on building a sales team. Success often hinges on how effectively a distributor can inspire others to join the ranks. Thus, the success of the organization relies heavily on the network’s expansion.
- Earnings Structure: In traditional sales, your paycheck is directly tied to your individual performance. Conversely, MLM structures allow members to receive a percentage of sales made at various levels of their network. This creates the potential for residual income, but it also raises questions about the true potential versus the realities faced by many.
In essence, while traditional sales reward individual effort, MLM rewards teamwork and recruitment capabilities, creating a complex interplay of incentives and motivations that keep participants engaged, for better or worse.
Considering these distinctions allows for a greater comprehension of the facets of MLM that attract investors. However, it also serves as a cautionary tale of potential traps hidden behind the promise of lucrative returns.
The Operational Mechanics of
The operational mechanics of multi-level marketing (MLM) form the backbone of its structure, driving its success, growth, and sometimes its downfall. It's vital for investors and enthusiasts alike to understand how these systems work in order to navigate the waters thoughtfully. By delving into the intricacies of recruitment, payment structures, and the balance between retail sales and recruitment, we can paint a clearer picture of what makes MLM tick — and where potential pitfalls might lie.
The Recruitment Process
At the heart of MLM is the recruitment process, which acts like the proverbial engine fueling the entire operation. New participants, often referred to as distributors or representatives, are recruited primarily based on personal connections. This means that friends, family, and social circles often become the initial target market. The allure of earning money and gaining financial freedom is a strong selling point that MLM proponents use to lure in new members.
However, the recruitment process is not without its complexities. Once someone joins, they aren't just expected to make sales; they are also encouraged to recruit others, thus creating a downline. This creates a multi-tiered structure where each participant earns a percentage of sales not only from their own efforts but also from the efforts of those they recruit. This can lead to rapid expansion but also raises questions about sustainability and ethics. The pressure to recruit can sometimes overshadow the quality of product sales, skimming the surface of what MLM was originally intended to be.
Payment Structures in
Understanding the payment structures in MLM is crucial for anyone considering investment in this field. Payment typically flows through various methods: commissions, bonuses, and incentives. Generally, participants earn money through retail sales and commissions on their downline’s sales. Often, companies will implement different compensation plans such as binary, uni-level, and matrix structures. Each one has its advantages and disadvantages, which can significantly affect potential earnings.
- Commissions: This is the bread and butter for MLM distributors; they earn a percentage from products sold direct to consumers. The percentage may vary based on the company's policies.
- Bonuses: Usually linked to performance metrics, bonuses can encourage higher sales and recruitment rates.
- Incentives: Sometimes companies offer luxury items, travel opportunities, or cash bonuses for surpassing sales quotas or recruiting a specific number of new members.
While these structures can be financially attractive, they often hinge heavily on the ability to expand one’s downline. This creates a hierarchy that can, in some instances, lead to dissatisfaction and feelings of being undervalued if participants don't see immediate results.
Role of Retail Sales vs. Recruiting
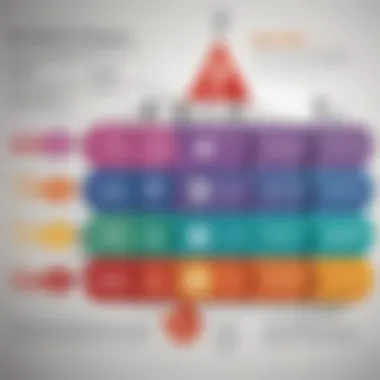
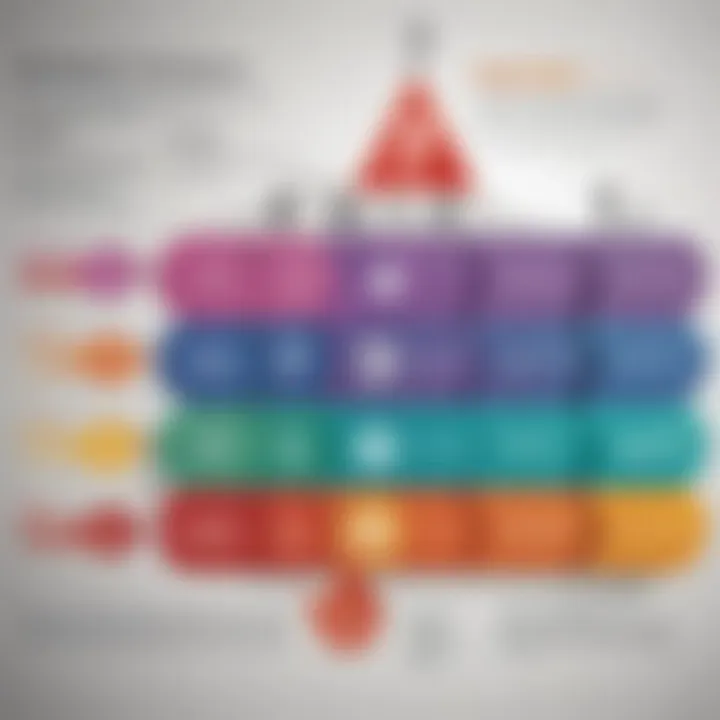
This brings us to the delicate balance between retail sales and recruiting. A successful MLM operation should, ideally, maintain a clear focus on product sales rather than solely on recruitment. Companies touting a legitimate business model often stress the importance of selling products to consumers rather than prioritizing the recruitment of new distributors. Unfortunately, this ideal doesn’t always play out in practice.
"In MLM, maintaining the harmony of retail sales and recruitment is like walking a tightrope; one misstep can lead to a fall."
While recruiting helps build the necessary downlines for revenue generation, overemphasis on recruitment can create the appearance of a pyramid scheme, where the focus is less on product sales and more on the influx of new members. This is not just a structural concern; it also corners investors with ethical dilemmas and reputational risks.
Understanding the mechanics behind MLM can equip investors and participants with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions. From recognizing the importance of effective recruitment strategies to acknowledging the ethical implications of recruitment versus sales, a comprehensive grasp of these aspects is vital for anyone looking to navigate the often murky waters of multi-level marketing.
Psychological Aspects of Participation
Understanding the psychological aspects behind participating in multi-level marketing is essential in grasping why individuals are drawn to these ventures despite their complexities. The motivations for people to join MLM schemes often encompass various personal and financial incentives, shaping their decision-making process and their ongoing engagement with the network. Furthermore, the role of social networks plays a significant influence on how MLM is perceived and how it operates within communities. This section delves into these psychological factors, revealing the underlying dynamics that can make MLM attractive but also potentially hazardous.
Motivations for Joining
Many people enter multi-level marketing with a set of expectations, some well-founded, while others are perhaps overly idealistic. The push factors vary from individual to individual, but usually, they can be categorized into several key motivations:
- Financial Freedom: Many individuals are attracted to MLMs in hopes of escaping the 9-to-5 grind or achieving financial independence. The allure of setting one's own hours and being one's own boss can be captivating.
- Community and Belonging: MLMs often emphasize community, portraying a family-like atmosphere. For people seeking connection or camaraderie, joining an MLM serves as an easy way to become part of a group.
- Personal Development: Some individuals are drawn by the promise of self-improvement through training programs that promise to enhance skills in sales, marketing, and person-to-person communication.
- Flexibility: With the potential to work from home or set your schedule, the flexibility that MLM offers can be a major selling point for those balancing personal responsibilities or pursuing side hustles.
However, it's crucial to acknowledge that these motivations might not always translate into success. The psychological aspect can lead to cognitive dissonance when expected outcomes do not align with actual experiences in the MLM arena. For instance, when faced with high-pressure tactics or unsustainable recruiting expectations, participants may grapple with their initial enthusiasm.
The Impact of Social Networks
Another significant aspect of MLM participation is the role of social networks. The very nature of multi-level marketing hinges on personal connections; often, individuals recruit friends or family into the business model. This social dynamic can have multifold impacts:
- Trust Factor: When friends and family are involved, there’s an inherent sense of trust that may not be present in traditional sales environments. This trust can make people more susceptible to participating in MLMs, even if the opportunity isn't as lucrative as advertised.
- Peer Pressure: Once involved, individuals may feel pressure to continue participating to maintain their relationships or to avoid disappointing those who recruited them. Sometimes it morphs into a sense of obligation rather than an informed choice.
- Information Cascades: People tend to seek advice from their social networks. If someone in their circle is successful in MLM, an echo chamber effect may encourage others to join, often leading to a false sense of security about the venture.
- Stigma and Resistance: Conversely, societal skepticism about MLMs can lead to social stigma. This means those in MLM networks may feel defensive about their choice, sometimes doubling down on their commitments as a way to justify their decisions to themselves and others.
In summary, the psychological landscape surrounding multi-level marketing is nuanced. Understanding these motivations and network effects is pivotal for investors and participants alike, as it unfolds the human element behind the business model. Recognizing and navigating these aspects can better equip potential members to make informed choices, helping them to discern whether the risks are worth the potential rewards.
Economic Implications of
When diving into the world of multi-level marketing (MLM), one must confront the economic nuances that come into play. This aspect is crucial because it informs potential participants about the possible rewards and hazards involved. Investors contemplating MLM need a solid grasp of how this business model operates within the broader marketplace. It isn’t just about selling products; it's a unique blend of networking, investment, and potential income that may not be immediately apparent.
Potential Earnings and Risks
Engaging in MLM offers a tantalizing prospect of income that can appear almost too good to be true. Many join these ventures with dreams of untold wealth, inspired by success stories shared in both local meetings and online forums. However, these potential earnings come with their share of risks.
- Earnings Potential: MLM participants often earn commissions on products sold, as well as bonuses for recruiting new members into their downline. For instance, Amway and Herbalife are well-known for their payment structures which reward both retail sales and recruitment efforts significantly. The appeal is in the promise that, as your network grows, so does your income.
- Diverse Outcomes: It’s worth noting that not everyone finds financial success through MLM. According to various reports, including those from the Direct Selling Association, a sizable portion of participants earn little to nothing. This presents a stark contrast where while some rake in substantial profits, many others may only see a trickle of income.
- Initial Investments: Most MLMs require upfront investments for starter kits and inventory. This can lead to financial strain, particularly if sales do not meet expectations. As the saying goes, "You have to spend money to make money," but in MLM, this can sometimes lead to a downward spiral.
- Market Saturation: As the network grows, the market for products may become saturated. This often results in a struggle to find new recruits or customers, further endangering potential earnings. Thus, it becomes vital for participants to continuously think outside the box to avoid a stagnant market.
In summary, while the potential earnings in MLM can be enticing, they are often paired with disproportionate risks and a significant learning curve. Understanding the financial dynamics at play can make the difference between thriving within a model or losing money along the way.
Comparing to Other Investment Strategies
When one considers MLM as an investment, it’s essential to compare it with traditional investment vehicles. While both may promise returns, the mechanisms and risk profiles can be vastly different.
Here are some critical comparisons:
- Stock Market: Unlike MLMs, where earnings largely stem from personal sales and recruitment, stock investments fluctuate based on company performance in the public market. The potential for loss exists in both, but in stock market investing, diversification can mitigate risks more effectively.
- Real Estate: Real estate can offer steady returns through rental income and appreciation, whereas MLM income streams can often be erratic. Additionally, real estate usually has well-defined legal protections and structures that MLM can sometimes lack.
- Peer-to-Peer Lending: This is another avenue where investors may earn returns, often at higher interest rates than traditional banks. However, in MLM, the risk often rests on an individual's ability to sell and recruit, which can vary widely.
- Cryptocurrency: As a newer investment strategy, cryptocurrencies share some similarities with MLM in terms of volatility. However, cryptocurrencies are driven by technology and market demand, rather than direct sales efforts and an ever-changing downline structure.
In closing, when evaluating MLM against diverse investment strategies, it’s clear that while the potential rewards exist, so do considerable risks. The unique structure of MLM demands careful consideration and due diligence before diving in.
Regulatory Considerations in


Understanding the regulatory landscape surrounding multi-level marketing (MLM) is crucial for anyone contemplating participation or investment in such programs. Regulatory considerations are not just about compliance; they protect consumers and legitimate businesses from potential fraud. By examining the legal constraints and enforcement mechanisms, investors can navigate the often murky waters of MLM arrangements, making informed decisions that align with their financial interests.
Legal Framework Governing
The legal framework that governs MLM activities varies widely from one jurisdiction to another. In the United States, for instance, MLMs operate under a broader umbrella of direct selling laws enforced by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). The FTC delineates acceptable marketing practices while also prohibiting deceptive or misleading promotional tactics. Crucially, this means that MLM companies must provide evidence of the income potential they advertise, ensuring that participants are not lured in by unrealistic promises.
In many countries, such as Canada or the UK, there are specific laws targeting pyramid schemes, which often masquerade as legitimate MLM ventures. These laws stipulate that MLM participants must earn their income primarily from retail sales rather than recruitment. This distinction is essential, as it clarifies what differentiates a lawful MLM from a pyramid scheme, which is illegal in most places.
The consequences of not adhering to these legal frameworks can be severe. Companies may face hefty fines, and participants may find their earnings wiped out if the program is shut down due to regulatory violations. Therefore, understanding these laws isn't just informative—it's a necessary step in safeguarding one's investment.
Regulatory Challenges and Enforcement
Navigating the regulatory landscape of MLM is rife with challenges. One significant hurdle is the enforcement of existing laws. While regulatory bodies like the FTC and equivalent organizations in other countries work diligently to monitor and penalize companies engaging in unethical practices, their reach can be limited. This limitation often results from the sheer number of MLM programs operating globally, leading to gaps in oversight.
Moreover, the dynamic nature of online marketing has further complicated enforcement efforts. Many MLM companies operate primarily through virtual platforms, utilizing social media for recruitment and product sales. This online presence often makes it challenging for regulators to track and monitor activities, as the rapid pace of digital commerce can outstrip legal responses.
"Many investors are drawn to MLM opportunities, but lack of awareness about regulatory issues can lead to significant financial loss."
Investors should be proactive in researching the legitimacy of an MLM program. This includes cross-referencing claims with regulatory findings and ensuring that the program complies with local laws. Furthermore, understanding the signs of potential wrongdoing can indicate whether a company is operating ethically or skirting legal requirements.
In summary, the value of a clear understanding of the regulatory framework cannot be overstated. It not only protects investors from being caught in fraudulent schemes but also helps maintain the integrity of the MLM model itself.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding
Exploring the ethical considerations surrounding multi-level marketing is crucial for anyone involved or contemplating involvement in this business model. The approach to marketing and recruitment within MLMs raises significant questions about fairness, transparency, and the true nature of success in such enterprises. It’s not just about the potential to earn money; it’s about how that potential is presented and pursued. As investors and potential participants dive into this world, understanding these ethical elements can shed light on what boundries can easily be crossed.
The Fine Line Between and Pyramid Schemes
Determining whether an MLM is a legitimate business opportunity or a pyramid scheme can be like navigating a minefield. While both structures offer compensation for recruitment, in a legal MLM, the primary focus should be on selling products or services. Pyramid schemes, conversely, unnecessarily tilt the scales heavily towards recruitment over product sales. Here are a few distinguishing factors that help clarify the boundary between these two:
- Product Viability: A legitimate MLM provides real products or services that possess intrinsic value, which can stand independently of the recruitment model.
- Commission Structure: In MLMs, commissions should primarily stem from product sales, not just recruitment bonuses. If the money flows more from signing up new members rather than selling products, it’s a red flag.
- Actual Retail Sales: Legitimate businesses typically require proof of sales to external customers rather than just to the participant's network.
Understanding these variances can serve as a foundation for ethical decision-making. Many start with bright ideas but end up straddling this fine line, which can lead to reputational damage and potential legal ramifications.
"The difference between an MLM and a pyramid scheme can be as thin as a slice of cheese, but it matters immensely where you place your hopes."
Manipulative Sales Techniques
The tactics employed in MLMs can often toe the ethical line, sometimes straying into questionable territory. Many affiliates are trained to employ techniques that encourage potential recruits to sign up without fully comprehending the associated risks. This can lead to an environment that prioritizes quantity of recruits over quality and ethical standards. A look at common manipulative sales techniques reveals the following:
- Exaggerating Potential Earnings: It’s common for some MLM presentations to highlight sky-high earnings that are achievable only by the minority, all while downplaying the average earnings, which often tell a starkly different story.
- Social Pressure: Many individuals might feel pressured to join or recruit based on emotional ties to friends or family who are already involved. This tactic can cloud judgment, making rational decision-making difficult.
- Promising Lifestyle Changes: MLMs often market success stories that showcase dramatic lifestyle changes, using glowing testimonials that may not reflect reality for the majority. This strategy capitalizes on dream-selling, potentially leading people to make financial commitments they cannot afford.
By recognizing these underlying manipulative sales techniques, potential investors can arm themselves with knowledge that can save them from potential regret and loss. Exploring ethical considerations not only enhances comprehension of MLM but also supports better decision-making during potential participation.
In summary, it is vital to approach multi-level marketing with a critical lens, holding companies responsible for their practices and ensuring one’s decisions align with personal values and ethical standards.
Technological Influence on
In today’s fast-paced world, technology plays an immense role in shaping various industries, and multi-level marketing (MLM) is no exception. Understanding how technology influences MLM is crucial for investors, financial advisors, and analysts who seek to navigate this multi-faceted and often misunderstood landscape. This section examines significant elements such as the use of social media and automation, both powerful tools that enhance reach and efficiency in recruitment.
The Use of Social Media in


Social media has entirely transformed how MLM companies operate by creating new avenues for marketing and networking. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok have become the digital marketplaces where aspirants promote their products and recruit new members. Companies leverage these platforms not merely to sell products, but to build communities.
- Wider Reach: Social media allows participants to tap into broad audiences. Instead of relying solely on face-to-face meetings, members can connect with potential recruits around the globe. This opens the door to new markets, especially in regions previously out of reach.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Traditional advertising can break the bank. Social media represents a budget-friendly alternative. Creating targeted ads, such as those on Facebook, can yield high returns on investment since they reach the chosen demographic.
- Engagement: Social media fosters engagement, allowing participants to share testimonials, success stories, and product demonstrations. This personal touch can effectively create a sense of authenticity and trust, which is essential in MLM.
"In MLM, where personal relationships are an integral part of the business, social media serves as the lifeblood for connecting individuals beyond geographical limitations."
However, it is vital to consider the potential pitfalls as well. Misleading promotions can lead to accusations of deception or even outright scams, hurting the business' reputation. For potential investors, it's essential to evaluate how effectively an MLM utilizes social media for both branding and attracting members.
Automation and Its Effects on Recruitment
Automation has been a game changer in the recruitment process for MLM companies. Leveraging software and digital tools can lead to more efficient operations and better-targeted recruitment efforts.
- Streamlined Processes: Processes like lead generation and follow-ups can be automated through CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems. This saves time, allowing participants to focus on personal interactions that matter.
- Data Analytics: Automation tools provide valuable insights into consumer behavior and preferences. By analyzing this data, MLM companies can tailor their pitches and enhance their marketing strategies accordingly.
- Recruitment Funnels: Automated recruitment funnels can guide potential recruits through a process that educates and converts them into active members, a noteworthy advancement compared to traditional methods.
In summary, technology has fundamentally altered the nature of MLM, allowing for enhanced reach, engagement, and efficiency in operations. The wise use of social media and automation can lead to substantial success in recruitment and ultimately, profitability. Investors should thus critically assess an MLM's technological integration to gauge its potential efficacy in the marketplace.
Evaluating Opportunities
Evaluating multi-level marketing opportunities is not just a precaution; it’s a discerning approach that can significantly influence profitable decision-making. For those contemplating a leap into an MLM venture, developing a clear understanding of what constitutes a legitimate opportunity is crucial. Like walking through a minefield, the multi-layered landscape of MLM can seem chaotic and treacherous. Untangling the web of claims and promises often requires a keen eye for detail and critical thinking skills. One must weigh not only the allure of potential earnings but also the reality check of the operational mechanics behind each offer.
Criteria for Legitimate Programs
When sifting through the myriad of MLMs available, there are several criteria that can help identify genuine companies. Here are some key elements to consider:
- Product Viability: A legitimate MLM should have tangible products or services that hold real market value—not just hype. Look for products that people would buy even if the business opportunity didn’t exist.
- Transparent Business Model: Clarity in how earnings are generated is vital. Legitimate MLM programs should clearly outline how commissions are earned and the specific metrics involved.
- No Mandatory Inventory Purchases: Avoid companies that require you to buy large amounts of inventory upfront. This is often a red flag pointing to potential pyramid scheme structures.
- Clear Compensation Plan: Understand the layout of the payment structure. A legitimate program will provide a detailed compensation plan that outlines how commissions and bonuses are earned.
- Strong Training and Support: Reliable companies tend to offer substantial training and ongoing support, helping their team members achieve success without veering into manipulative sales tactics.
Red Flags to Watch For
Not every shining opportunity is golden. There are certain warning signs that can indicate a possibly problematic MLM. Pay attention to the following:
- Overemphasis on Recruitment Over Sales: If the primary focus is on recruiting instead of selling products, there’s a strong likelihood the operation may not be legitimate.
- High Entry Costs: When joining an MLM requires a significant upfront investment with little clarity on how these funds are utilized, tread carefully.
- Pressure Tactics: Watch for companies that employ high-pressure sales techniques or create an atmosphere of urgency to enroll new members. This can often lead to hasty, ill-informed decisions.
- Lack of Verifiable Success Stories: Be skeptical of claims that everyone involved gets rich. If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is. Inquire about real-life success stories that can be verified.
- Poor Marketplace Reputation: Conduct research on the company. Online platforms like Reddit or dedicated MLM forums can provide insights into others' experiences, shedding light on potential pitfalls.
Keep in mind that diligence is key. It’s essential to pause, reflect, and thoroughly investigate before you dive headfirst into any MLM venture.
To sum it up, navigating MLM opportunities requires acumen and a discerning mindset. By adopting a meticulous approach to evaluation and being aware of both potential benefits and pitfalls, investors can significantly bolster their chances of finding a legitimate and rewarding opportunity.
End: Navigating the Landscape
As we wrap our journey through the perplexing terrain of multi-level marketing (MLM), it becomes clear that there are many layers to this business model. The conclusion of this exploration is not merely a recapitulation but a vital component in helping investors and participants navigate the labyrinthine aspects of MLM. This section underscores critical considerations for making informed decisions, understanding the risks involved, and recognizing viable opportunities within this space.
Summary of Key Insights
Throughout this article, several fundamental insights emerge, shedding light on the operation and implications of MLM. Here are the primary takeaways:
- Complex Structure: MLM operates on a layered system comprising product sales and recruitment, where the latter often supplements income.
- Psychological Dynamics: Participants are frequently motivated by both social connections and personal aspirations, which can affect their engagement and outcomes.
- Economic Risks: The potential for earnings exists, but it’s essential to recognize the inherent risks and the reality that many participants do not achieve significant income.
- Regulatory Landscape: Understanding the legal frameworks governing MLM can help ascertain the legitimacy of a program and its practices, providing essential protective measures as one engages in MLM.
- Ethical Alignments: Differentiating between ethical MLM practices and others that may tread close to the line of pyramid schemes is crucial for maintaining integrity in business dealings.
- Tech Influence: Modern technology and social media can amplify recruitment efforts but might also contribute to fraudulent practices if not approached with discernment.
"Navigating the MLM landscape requires not just knowledge of techniques, but a firm grasp of the underlying ethical and legal considerations that govern it."
Now, what does this mean for you? In short, being well-informed is your best strategy.
Final Thoughts on Participation
Engaging in MLM requires a balanced approach informed by thorough due diligence. Here are a few final considerations to keep in mind:
- Research and Reflect: Before diving in, take the time to study the specific MLM program. Look for transparent operations, realistic earning potentials, and the experiences of others involved. Forums on platforms like Reddit or Facebook can provide candid insights from actual participants.
- Strategic Networking: If you decide to participate, consider the role your personal network plays in your success. Building trust and a strong relationship with your prospects can lead to better outcomes.
- Recognize Limitations: It's crucial to acknowledge that success in MLM does not come effortlessly. High turnover rates among participants signal that strategies successful for some may not translate to everyone.
- Learn Continuously: Stay abreast of market trends and regulatory changes. The landscape isn't static, and being adaptable will enable you to navigate future shifts more effectively.
Ultimately, MLM can be a legitimate avenue for those who approach it with the right mindset and tools. However, awareness of the potential pitfalls is equally important to sidestep challenges that could prove detrimental. Thorough understanding and reflection will guide you through the complex world of multi-level marketing.
Always remember that knowledge is power, especially in a venture that can be as dynamic as MLM.







